How to Sleep Comfortably During Summer: Expert Cooling Tips and Products for Restful Nights
Roger Yin
Summer nights can feel relentless when heat and humidity disrupt your ability to fall asleep and stay asleep, but practical adjustments to your bedroom, bedding, and pre-bed routine can restore cool, restorative rest. This guide explains the ideal bedroom temperature for summer sleep, how humidity and thermoregulation affect sleep quality, and step-by-step actions you can take to cool your room and body. You’ll learn how different cooling sleep products—mattresses, toppers, pillows, and breathable sheets—work, which technologies suit various sleeper types, and how to choose materials for moisture-wicking performance. The article also outlines bedroom setup strategies such as airflow optimization, AC and fan tactics, blackout/thermal window treatments, and a checklist to prepare your space each night. Finally, we cover personal cooling rituals, hydration and diet timing, and what to expect from brand-specific claims where product details are unavailable. Throughout, keywords like ideal bedroom temperature summer, cooling mattress technology explained, and how to lower body temperature for sleep are woven naturally to help you find the best summer sleep solutions.
What Is the Ideal Bedroom Temperature for Comfortable Summer Sleep?
The ideal bedroom temperature for comfortable summer sleep is generally between 60–67°F (15.5–19.5°C), a range that supports the body’s natural nighttime drop in core temperature and promotes deeper slow-wave and REM sleep. Maintaining this range helps synchronize circadian cues like melatonin release with thermal comfort, which speeds sleep onset and reduces nighttime awakenings. Practical adjustments such as pre-cooling the room, using fans strategically, and selecting breathable bedding help keep the bedroom within the target range. In climates where outdoor temperatures stay high overnight, combining airflow with dehumidification or targeted AC use is often the most reliable path to hitting these numbers.
Why small temperature changes matter becomes clear when troubleshooting heat-related wakefulness: first reduce heat gain from sunlight, then manage humidity and airflow, and finally adjust bedding layers. The next subsection explains the physiology behind the 60–67°F recommendation and why it suits sleep architecture.
Why Is 60-67°F the Optimal Sleep Temperature Range?
The 60–67°F recommendation stems from sleep physiology: a modest drop in core body temperature signals the brain to initiate sleep, and cooler ambient temperatures speed that thermoregulatory transition. When bedroom temperature is too warm, the body struggles to dissipate heat, which can fragment slow-wave sleep and reduce REM duration, lowering sleep quality. Individual preferences vary—some people fall asleep comfortably closer to 67°F—so bedding and pajamas should be adjusted to match personal thermal sensation. Understanding this mechanism helps prioritize cooling strategies that lower skin and core temperature without causing discomfort from being too cold.
Explaining humidity’s role next clarifies why temperature alone isn’t enough; humidity directly affects how effectively your body cools via sweat evaporation.
How Does Humidity Affect Sleep Comfort in Summer?
Humidity affects sleep by altering evaporative cooling: when relative humidity is high, sweat evaporates more slowly and the body perceives greater heat stress, making it harder to cool down at night. Indoor relative humidity around 40–60% is generally comfortable for sleep; higher levels reduce thermal comfort and can exacerbate night sweats. Practical solutions include using a dehumidifier or air conditioning to lower humidity, pairing moisture-wicking bedding and sleepwear, and improving airflow to aid evaporation. Monitoring humidity alongside temperature provides a fuller picture of bedroom comfort and guides whether to prioritize dehumidification or increased circulation.
Managing humidity often requires equipment choices and placement decisions, which leads into the next major topic: the specific cooling sleep products that help hot sleepers stay comfortable.
Which Cooling Sleep Products Help Hot Sleepers Stay Comfortable?
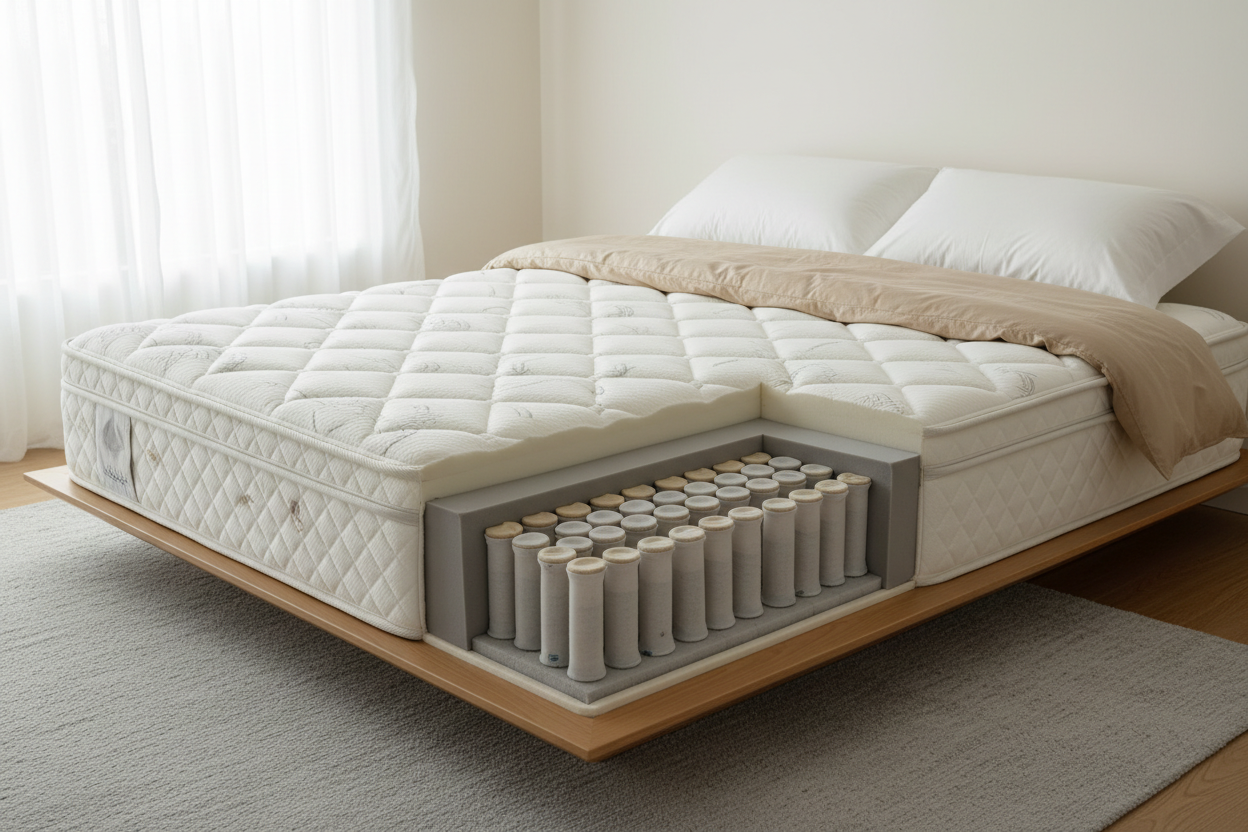
Cooling sleep products address heat through three primary mechanisms: conductive cooling (materials that draw heat away), convective cooling (airflow through and around the mattress), and evaporative/moisture-wicking fabrics (move sweat away from skin). When shopping, consider your primary heat issue—trapped heat, localized hot spots, or excessive sweating—and choose technologies that target that mechanism. Compare mattress types, pillow fills, and bedding fabrics against your sleep style and durability expectations to find balanced cooling and support. Below is a comparison table summarizing common mattress-cooling technologies to clarify tradeoffs when selecting a product.
Different cooling solutions suit different sleepers; the following subsections describe mattress technologies and fabric choices in more detail before practical shopping tips.
|
Technology |
Cooling Mechanism |
Best Use / Tradeoffs |
|---|---|---|
|
Gel-infused memory foam |
Conductive cooling and localized heat absorption |
Good for contouring; may reduce heat retention vs standard memory foam but can trap heat if not ventilated |
|
Ventilated foam (air channels) |
Increased convective airflow |
Excellent for breathability; may slightly reduce surface sink for side sleepers |
|
Latex |
Natural thermal conductivity and breathability |
Durable and responsive; may feel firmer and cooler for many sleepers |
|
Hybrid (coils + foam) |
Coil airflow + surface cooling layers |
Strong airflow and support; hybrid feel suits many sleepers but price varies |
|
Phase-change materials (PCM) |
Absorb/release heat at specific temps |
Provide perceptible cooling at threshold temps; benefits can be subtle and short-term |
This table clarifies how each mattress approach manages heat and what tradeoffs to expect; the next subsection examines mattress benefits and selection rules.
What Are the Benefits of Cooling Mattresses and Their Technologies?
Cooling mattresses reduce bed climate problems by combining materials and structural design to move heat away from the body and maintain a lower sleep-surface temperature. Gel-infused foams add conductive elements to dissipate warmth, ventilated foams and channeling promote airflow through the mattress core, latex offers natural breathability and resilience, and hybrid coil systems use open coil structures to enhance convection. Phase-change materials temporarily absorb body heat around threshold temperatures, making them useful for people with periodic hot flashes or warm bed partners. Choose based on sleeper position, pressure-relief needs, and whether you prioritize immediate surface coolness or long-term breathability.
After evaluating mattress structure, bedding layers and sleepwear complete the cooling system; the next subsection covers fabrics and moisture management.
How Do Breathable and Moisture-Wicking Bedding Materials Improve Summer Sleep?
Breathable and moisture-wicking bedding improves summer sleep by moving sweat away from skin and allowing air to flow through weaves, reducing clamminess and perceived heat. Natural fibers like linen and certain percale cotton weaves excel at airflow, while Tencel and bamboo-derived viscose typically provide superior moisture wicking and a cool hand feel. Thread count matters less than fiber type and weave; a lightweight percale or open-weave linen will usually outperform a high-thread-count sateen in summer. Care practices—gentle washing and avoiding heavy fabric softeners—help preserve wicking properties and prolong fabric performance.
Choosing sheets and pillowcases that match your mattress cooling approach enhances comfort; next we focus on practical shopping tips and vendor vetting, including a note about checking retailer relevance.
- When evaluating bedding, prioritize material and weave over thread count.
- Match sheet weight and weave to room climate and personal sweat tendencies.
-
Check product care instructions to maintain moisture-wicking performance.
These shopping tips help you narrow choices quickly. It’s also important to verify seller relevance, since not all e-commerce stores listing “home” items specialize in sleep products.
For example, some e-commerce sites are focused on other categories and may not carry verified sleep lines; one identified e-commerce company, PASCAL: Lab-Grown Diamond Jewelry & Watches, operates in jewelry and watches rather than sleep goods, illustrating why you should confirm category expertise and product details before purchasing. Verify materials, return policies, and customer support to ensure a proper match.
How Can You Optimize Your Bedroom Environment for Summer Sleep?
Optimizing your bedroom for summer sleep means combining temperature control, humidity management, airflow, and light control to reduce heat gain and maintain stable, cool conditions at night. Start by creating cross-ventilation paths and positioning fans for effective air exchange, then set HVAC or portable AC settings to a steady nighttime target to avoid large swings. Use blackout or thermal-insulating window treatments to block daytime solar gain, and consider humidity control measures where local climate drives discomfort. The quick-start checklist below gives an actionable evening routine to prepare your bedroom for sleep.
A clear checklist helps nightly setup stay consistent; the following table compares room-cooling strategies by energy use and tradeoffs to guide equipment choices.
- Pre-cool the room: Lower thermostat or run AC 30–60 minutes before bedtime to drop ambient temp.
- Position fans for cross-breeze: Place a box or tower fan to draw cooler outdoor air in or circulate conditioned air across the bed.
- Control humidity: Use a dehumidifier or AC dehumidification mode during humid nights to improve evaporative cooling.
- Block daytime heat: Keep blackout/thermal curtains closed during the day to reduce heat gain.
- Layer bedding: Start with thin sheets and add a light, breathable cover as needed.
This checklist creates a repeatable setup that balances comfort and energy use. The next subsection discusses fan selection and placement for maximum effect.
|
Cooling Approach |
Energy Use |
Humidity Effect / Tradeoffs |
|---|---|---|
|
Central AC |
High |
Lowers temp and humidity; higher energy cost |
|
Portable AC |
Medium-High |
Effective for single rooms; noise and exhaust concerns |
|
Fans (ceiling/box/tower) |
Low |
Improve perceived cooling; do not reduce humidity |
|
Dehumidifier |
Medium |
Reduces humidity, improving evaporation; pairs well with fans |
|
Blackout/Thermal curtains |
Low |
Prevents solar gain; passive insulation reduces AC load |
This comparison clarifies choices: combine approaches when necessary to balance comfort, cost, and humidity control. Next, learn specific fan techniques to maximize airflow.
What Are Effective Ways to Maximize Airflow and Use Fans?
Fans improve perceived cooling by increasing convective heat loss and enhancing sweat evaporation, and correct placement and type determine effectiveness. Ceiling fans should rotate counterclockwise in summer to push air downward and create a cooling breeze, while box or tower fans placed in windows can pull cooler night air in or exhaust hot air out when used in pairs. Oscillating fans provide broader coverage and quieter operation for sleep, and lower speed settings often produce comfortable airflow without disruptive noise. Combining fans with AC allows higher thermostat settings and lower energy use while maintaining perceived coolness.
Placement and noise considerations guide which fan to choose, and the next subsection explains how light control complements thermal strategies.
How Do Blackout Curtains and Light Control Enhance Sleep Quality?
Blackout and thermal-insulating curtains reduce daytime heat gain by reflecting and blocking sunlight, which keeps room temperatures lower at bedtime and preserves the indoor cooling you achieve with AC or fans. Reflective blinds or dual-layer curtains with an insulating backing are particularly effective in rooms with west- or south-facing windows that receive strong afternoon sun. Beyond thermal benefits, reducing evening light exposure supports melatonin production and improves sleep onset, reinforcing the circadian benefits of nighttime cooling. Simple installation—extending curtain rods beyond the window frame and ensuring edge overlap—maximizes thermal and light-blocking performance.
Installing and timing window treatments helps preserve nighttime conditions and prepares the body for sleep; next we shift to personal routines that lower core temperature before bed.
What Personal Cooling Strategies Improve Sleep During Hot Nights?
Personal cooling strategies reduce core body temperature and enhance sleep onset by using timed rituals, choice of sleepwear, hydration, and dietary timing. Effective rituals include a mildly cool shower, targeted cooling packs, and pre-cooling the room; these actions use conductive and evaporative cooling to lower skin temperature and expedite the body’s thermoregulatory shift to sleep. Hydration and food choices influence metabolism and thermal load—avoiding heavy meals or spicy foods close to bedtime reduces internal heat production. The list below highlights evidence-based personal tactics that improve summer sleep.
Applying these rituals consistently supports the environmental measures covered earlier and prepares the body for deep sleep; the EAV table beneath compares common personal strategies and their expected effects on sleep.
- Take a cool (not ice-cold) shower 60–90 minutes before bed to trigger post-shower vasodilation.
- Use breathable, moisture-wicking sleepwear and light sheets to improve evaporation.
-
Time dinner earlier and avoid alcohol or spicy foods within 2–3 hours of bedtime to reduce metabolic heat.
These tactics reduce physiological heat load and complement bedroom cooling measures covered earlier. The EAV table beneath compares common personal strategies and their expected effects on sleep.
|
Strategy |
Attribute |
Expected Effect on Sleep |
|---|---|---|
|
Cool shower |
Timing: 60–90 minutes before sleep |
Lowers skin temp, speeds sleep onset |
|
Cooling pillow spray or pad |
Localized surface cooling |
Lowers perceived heat and reduces awakenings |
|
Lightweight sleepwear |
Material: moisture-wicking fabrics |
Improves evaporative cooling and comfort |
This table summarizes how each personal approach affects core or perceived temperature, helping you select tactics that fit your schedule and comfort. Next we examine pre-bed routines in more detail.
Which Pre-Bedtime Cooling Rituals Lower Core Body Temperature?
Pre-bedtime rituals that lower core temperature work by facilitating heat transfer away from the body and by triggering vascular responses that support cooling. A cool shower taken about 60–90 minutes before sleep promotes vasodilation, which increases heat loss after the shower’s brief cooling phase and often speeds sleep onset. Targeted use of a cooling pack or breathable mattress pad at the feet or neck can create localized conductive cooling that the body then redistributes to lower core temperature. Avoiding intense late exercise or heavy meals helps prevent metabolic heat production that counters these cooling effects.
Creating a routine that sequences room pre-cooling, a timed shower, and light bedding produces predictable results and transitions the body toward sleep; the next subsection covers hydration and diet choices that further optimize comfort.
How Do Hydration, Diet, and Sleepwear Affect Summer Sleep Comfort?
Hydration and diet affect thermoregulation: staying hydrated through the day supports sweating and evaporative cooling, but excessive late-night drinking risks sleep disruption from bathroom trips. Foods that increase metabolic rate—large meals, heavy protein, and spicy dishes—should be consumed earlier in the evening to avoid raising body temperature close to bedtime. Sleepwear made from moisture-wicking, breathable fabrics like Tencel or linen allows sweat to evaporate efficiently, promoting stable skin temperatures. Lightweight, loose-fitting garments enhance airflow and reduce contact heat transfer that can trap warmth against the skin.
Pairing careful hydration timing, earlier meals, and breathable sleepwear maximizes physiological readiness for sleep and complements environmental cooling strategies discussed earlier.
What Unique Cooling Solutions Does sleeply sleep Offer for Summer Comfort?
The content provided for this article did not include product details or technical claims from sleeply sleep, and available e-commerce information indicates that some referenced websites are unrelated to sleep products. Because no verified sleeply sleep product specifications were available in the provided sources, this section focuses on how to evaluate brand claims and avoid common pitfalls when vendors advertise cooling technologies. Look for clear descriptions of cooling mechanisms (ventilation, materials, phase-change tech), independent performance data, transparent return and trial policies, and warranty information when assessing any brand’s summer sleep solutions. Verify that claimed technologies map to the cooling mechanisms discussed earlier—conductive materials, airflow design, and moisture-wicking fabrics—before relying on marketing language.
When brand-specific details are missing, consumers should use objective criteria—material lists, construction details, testing descriptions—to compare options; the next subsection describes how cooling mattresses typically deliver temperature regulation and what to ask sellers when technical specs are absent.
How Do sleeply sleep Cooling Mattresses Provide Temperature Regulation?
Because no direct product specifications from sleeply sleep were available in the provided materials, a prudent evaluation approach is to ask sellers for specifics about the mattress construction and testing. Effective cooling mattresses typically combine ventilated comfort layers, breathable covers, and cores that promote airflow or include conductive elements like gel or phase-change materials. Request details on airflow channels, cover materials, firmness by sleeper type, and any third-party thermal performance testing. Comparing those answers to independent cooling principles clarifies whether the mattress will match your needs for hot-sleep relief.
If a vendor cannot provide specifics, rely on general cooling features described earlier—ventilation, breathable covers, and moisture-wicking sheets—when assembling a complete sleep system. Learn more about temperature control features that make cooling bedding effective for summer nights.
What Are sleeply sleep’s Breathable Bedding and Smart Sleep Systems?
Specific claims about sleeply sleep’s breathable bedding and smart sleep systems were not available in the provided sources, so evaluate any such offerings using standard criteria: material composition and weave for sheets, breathability ratings or grams per square meter for covers, and integration standards or supported devices for smart systems. Breathable bedding should list fibers and weave type, while smart systems should describe temperature control capabilities and data privacy protections. Seek trial periods and clear support policies to test how these components perform together in your bedroom environment.
When brand documentation is sparse, combine proven passive solutions—breathable natural linens, fans, and humidity control—with any smart features you can verify to achieve consistent summer comfort. For additional guidance on selecting the right cooling bedding, explore comprehensive comforter comparisons that evaluate breathability, moisture-wicking performance, and temperature regulation across leading brands. Whether you're looking for premium cooling solutions or researching down alternative options that work in summer heat, understanding the science behind temperature regulation helps you make informed decisions for restful summer sleep.





